Many Organizations today are vulnerable to cyber-attacks and on an average, vulnerabilities have been active in organizations for more than 126 days even before they are discovered. Cyber Security is of paramount importance for all the Organizations especially with the kind of data breaches seen recently. Cyber-attacks from ‘Ransomware’, ‘Wanna Cry’, ‘Not Petya’, Crypto Jacking and others have put organizations like Telefonica, Maersk and others under heavy loss. A well planned and executed Cyber Security Strategy can help organizations to prevent Cyber Incidents. Ability to track and continuously reduce Mean Time to Remediate Vulnerabilities (MTTR) across the organization is a key factor that contributes to reducing the overall security risk.
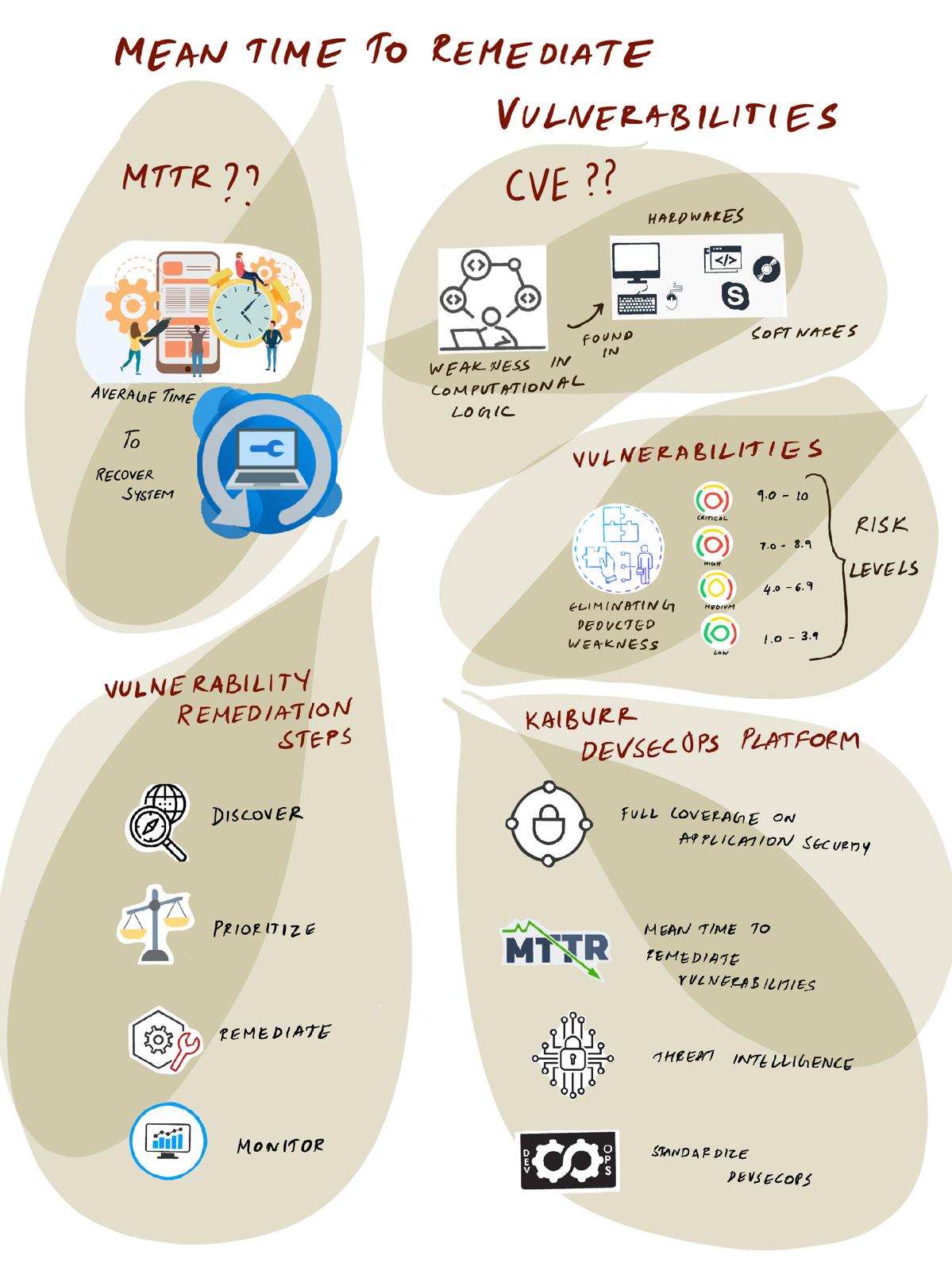
CVE (The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) program catalogs publicly disclosed cyber security Vulnerabilities and they define Vulnerability as “A weakness in the computational logic (e.g., code) found in software and hardware components that, when exploited, results in a negative impact to confidentiality, integrity, or availability. Mitigation of the vulnerabilities in this context typically involves coding changes, but could also include specification changes or even specification deprecations (e.g., removal of affected protocols or functionality in their entirety).”
Vulnerability remediation is a process of eliminating detected weaknesses in our Network, Computational environment and Software Applications. Vulnerabilities management includes the discovery, prioritization, remediation, and monitoring of a vulnerability to ensure a successful long-term fix. It delivers an actionable outcome for enhanced security.
The metric ‘Mean Time to Remediate Vulnerabilities’ is the average time taken to resolve vulnerability issues from the time they are identified.
Vulnerabilities are classified by their risk levels: Critical, High, Medium and low.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) ranks vulnerabilities published in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) on a scale of 1-10. A CVSS score of 0.1 to 3.9 earns a severity rating of Low; from 4.0 to 6.9 gets a Medium rating; 7.0 to 8.9 is rated High; and 9.0 to 10 is Critical.
The MTTR only includes closed vulnerabilities – it does not include false positives, accepted risks, or open vulnerabilities.
In Software product organizations, products continue to generate revenues and they also carry the risk of vulnerabilities. Cost of remediation is very high if they are shipped with vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities in a product can jeopardize the organization and can risk their very existence. Organizations that have good cyber security practices are cyber safe, have Competitive Advantage in the market, thrive on their brand value and executives in the organization can be assured Stress-free life. Such Cyber Resilient Organizations have low MTTR.
Vulnerability Remediation Steps:

Traditional remediation can increase the mean time to respond and leaves systems vulnerable for long amounts of time, which is totally unnecessary. Following a framework like the one mentioned below should help organizations to remediate vulnerabilities proactively, effectively and in less time.
- Discover – identify vulnerabilities through testing and scanning as part of the CI-CD process
- A vulnerability assessment systematically evaluates your system, looking for security weaknesses and vulnerabilities. This provides information to the security team to classify, prioritize, and remediate weaknesses. A good vulnerability assessment is a prime activity in risk management. Nearly 98% of cyber attackers exploit known vulnerabilities. 15000+ new vulnerabilities are discovered each year. Robust vulnerability assessment can help us eliminate Security weaknesses and be more cyber safe.
- Prioritize – classify vulnerabilities and assess risk
- The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is used by several organizations in order to communicate the vulnerability’s severity and characteristics. The CVSS scoring system calculates severity based on the attack vector, complexity, and impact.
- Remediate – block, patch, remove components, address vulnerabilities
- Monitor – look out for new vulnerabilities and weaknesses
- Retesting post fixes and continuous testing on changes is important to validate if the actions to remediate have yielded the required results.
Organizations need to shift their view of cyber crimes and remediations of vulnerabilities from a chaotic, random set of events to a more structured, predictable set of engagements and processes. Several security tools like JFrog x-ray, Aquasec, PrismaCloud, Blackduck, Coverity, Synk, Veracode, Fortify, Checkmarx etc., are very effective in scanning the code, binaries or images to identify Vulnerabilities and classify their risk exposure as either Critical, High, Medium or Low.
Kaiburr’s DevSecOps platform helps with the following –
- Enabling full coverage on application security testing (SAST, DAST, SCA, Image Scan, SBOM, Secrets)
- Reducing Mean Time to Remediate Vulnerabilities by prioritizing critical vulnerabilities for developers
- Reducing Security Risk with threat intelligence and near real time Security Risk Score at Organization, Portfolio and Application level.
- Standardize DevSecOps processes across the organizations by validating best practices
- Ensure effective use of application security tools to show ROI on tool investments
Sample Stage Gate Governance View in Kaiburr:

This helps to make sure nothing falls through the cracks in the software delivery process and critical vulnerabilities are bubbled up to developers near real time.
Sample Security Risk Score in Kaiburr:

This helps digital, engineering and security leaders to understand the current level of security risk based on open vulnerabilities so they could prioritize and remediate high risk vulnerabilities faster.
Reach us at contact@kaiburr.com to improve the mean to remediate vulnerabilities in your organization, accelerate your devsecops maturity and reduce the overall security risk.
